Best Practices in Teaching and Learning Methods
I. Teaching methods:
In our institution, teaching medical students involves a well-rounded approach that combines didactic lectures, clinical experience, practical skills training, and interactive learning. The following practices are integral to our educational strategy:
Lectures and Seminars:
• Foundational lectures begin with covering key topics in Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, and basic concepts across all disciplines.
• Multimedia presentations, videos, and interactive tools are regularly used to engage students effectively.
• Seminars are organized to allow for in-depth discussions on specific topics, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving.
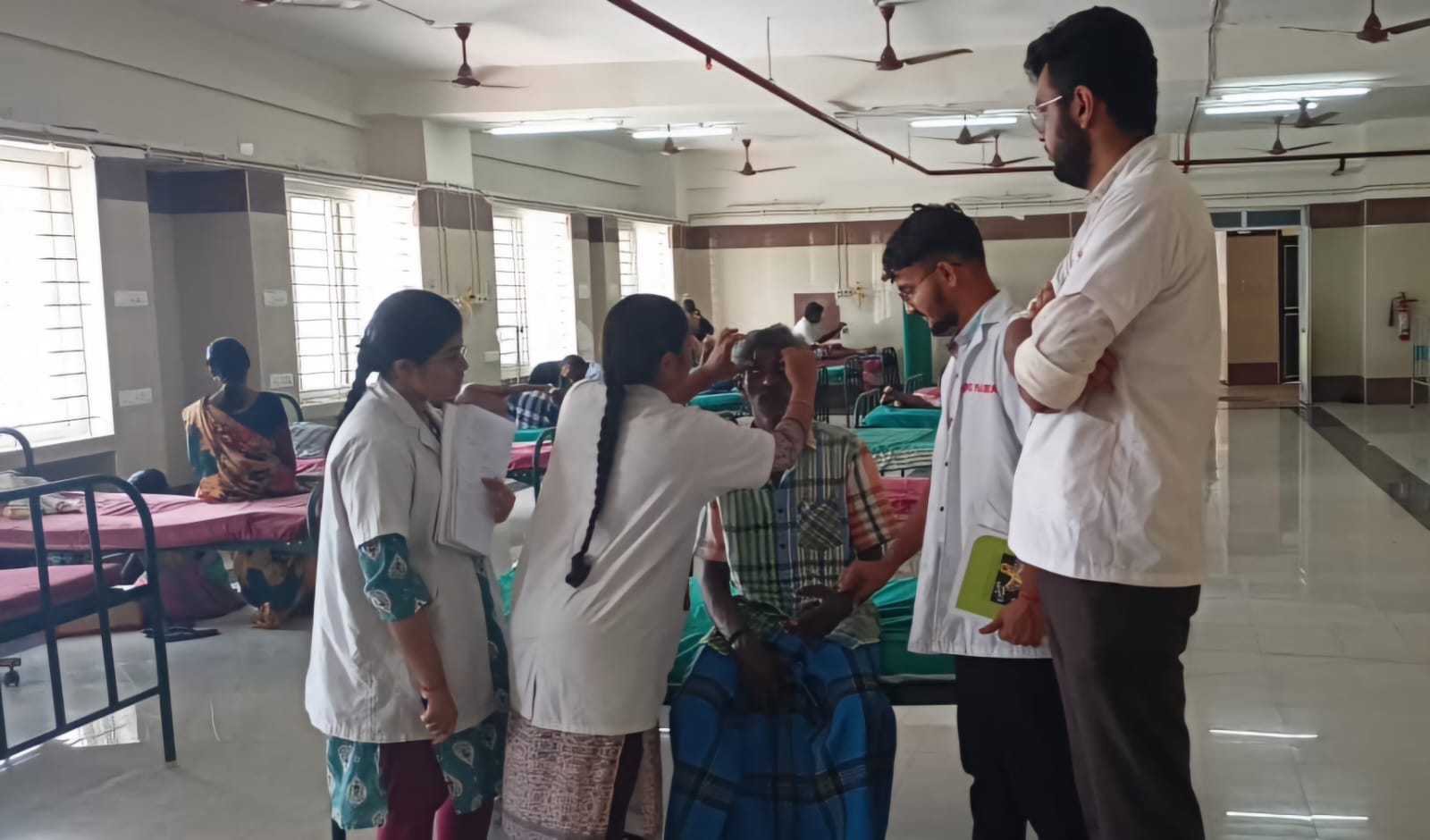
Clinical Exposure:
• Clinical exposure is regarded as crucial for student learning.
• Active participation, observation, and interaction with patients and healthcare providers are highly encouraged.
• Preceptors consistently provide guidance, feedback, and opportunities for case presentations.

Integrated Teaching:
• A holistic approach is fostered by integrating basic sciences with clinical practice.
• Interdisciplinary sessions are held to link concepts across various subjects.
• Active learning is promoted through team-based approaches that incorporate different specialties.
Case-Based Learning:
• Real patient cases are used to teach clinical reasoning and decision-making skills.
• Students are encouraged to discuss cases, identify key issues, and develop management plans.
• These case discussions take place in small groups or online forums.
Hands-On Skills Workshops:
• Practical training is provided in essential skills such as pelvic examinations, pap smears, suturing, Ryles tube insertion, and catheterization.
• Students are given opportunities to practice these skills on models or simulated patients.
Interactive Learning:
• Interactive tools and quizzes are used regularly for self-assessment and reinforcement of knowledge.
• Using platforms such as google classroom for group learning.
• Platforms like Google Classroom are utilized for group learning activities.
• Students are engaged in discussions and debates on ethical and controversial topics across all subjects.
Problem-Based Learning (PBL):
• PBL sessions are conducted where students work collaboratively to solve clinical problems or cases.
• Group discussions are facilitated to encourage critical thinking and application of knowledge.
Peer and Near Peer learning:
• Peer and near-peer mentoring is actively practiced, offering a collaborative learning experience.
Multidisciplinary Training:
• Collaboration with other departments is a key aspect of our multidisciplinary training approach.
Objective Structured Practical Examination (OSPE):
• OSPEs are conducted through a series of stations, each designed to assess specific practical skills or knowledge areas. These stations simulate real-life scenarios or laboratory tasks relevant to the students' field of study.
Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE):
• OSCEs are conducted to assess clinical skills and knowledge, with stations designed to mimic real clinical scenarios.
Continual Assessment:
• Regular quizzes, exams, and formative assessments are used to monitor student progress, with timely feedback provided to support their improvement.
Patient-Centered Care:
• The importance of patient communication, empathy, and cultural sensitivity is emphasized throughout the curriculum.
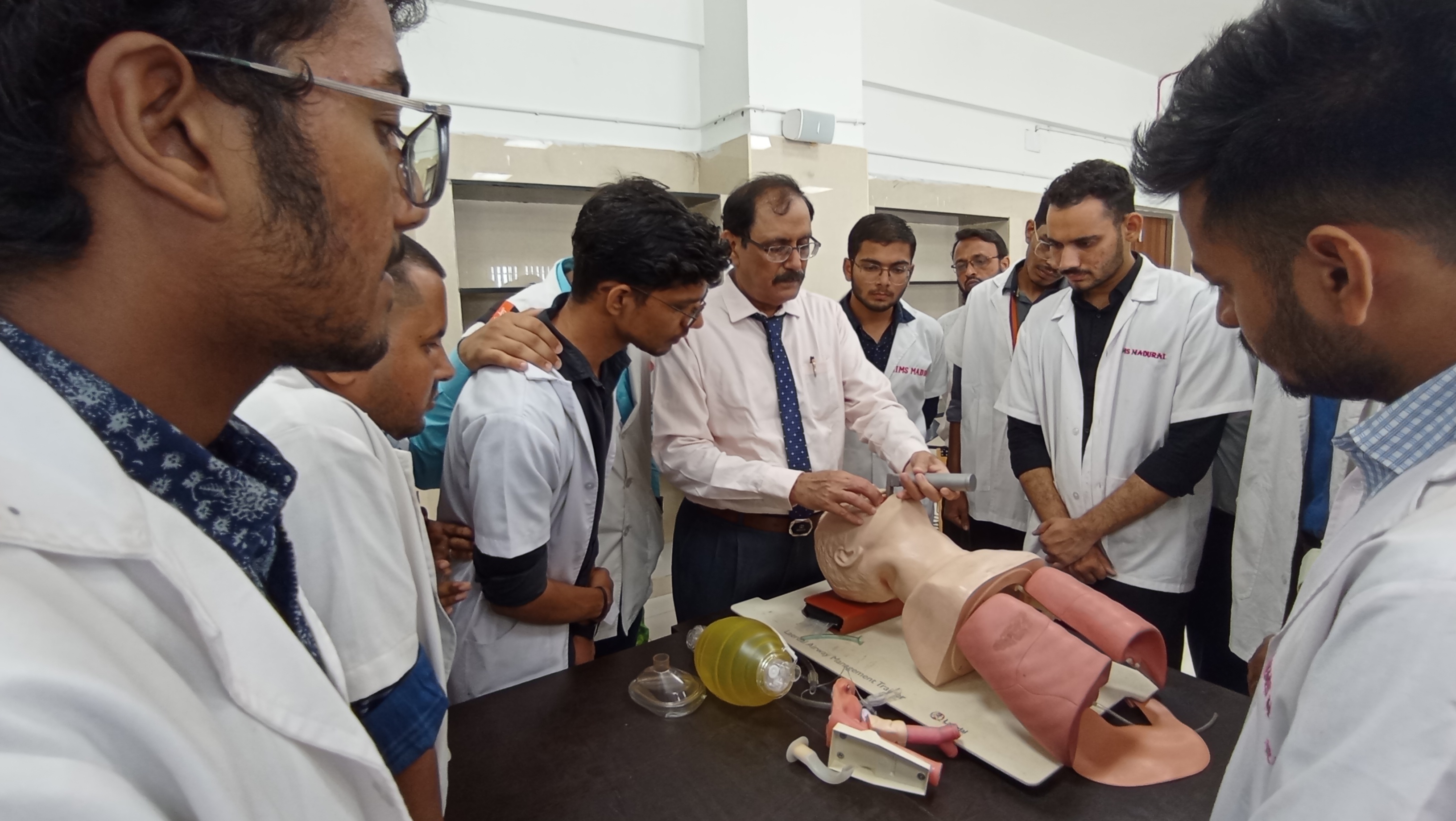
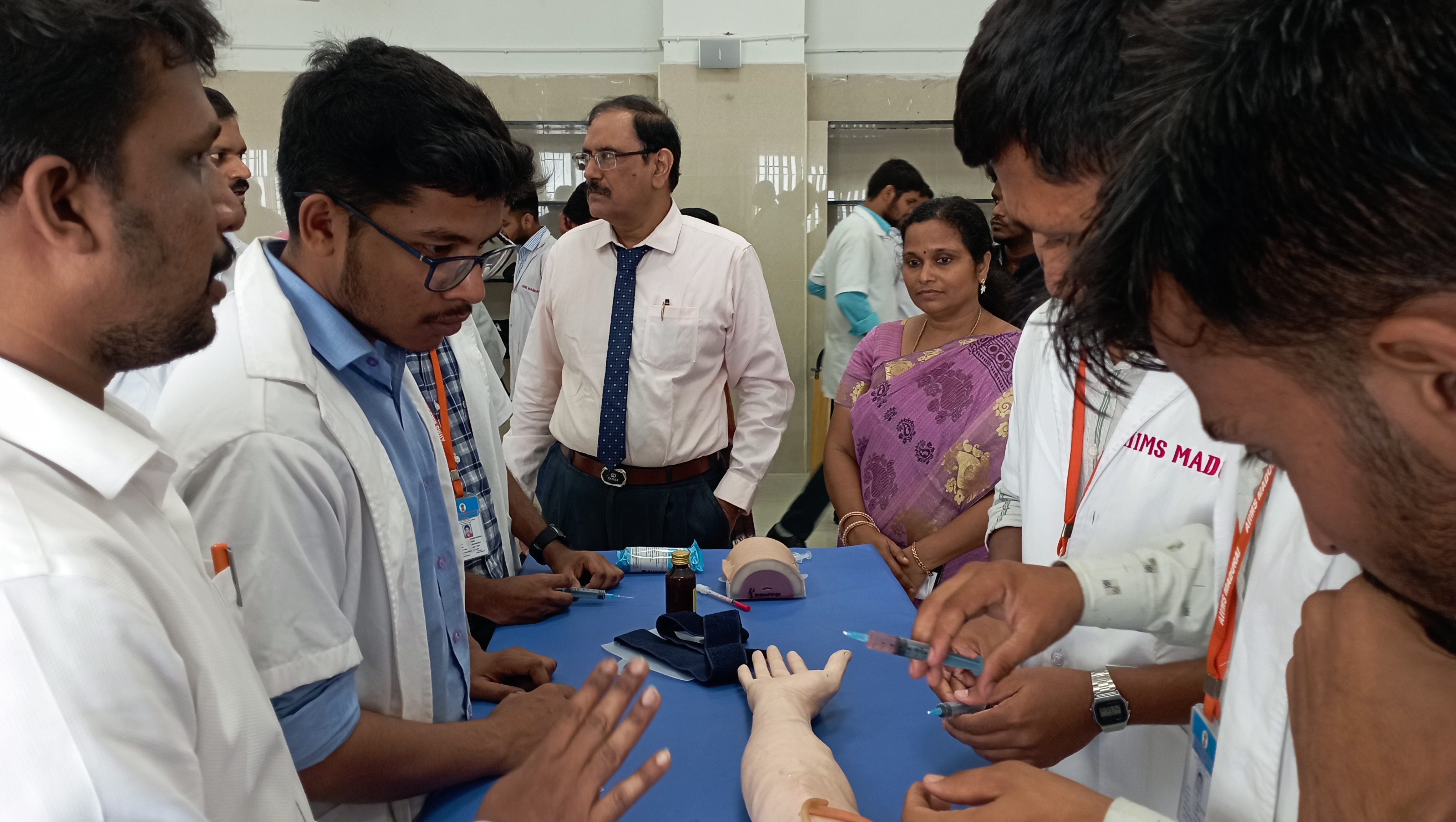
Simulation Training:
• Simulation-based learning is incorporated through the use of mannequins.
• Scenarios such as normal deliveries, emergency situations, and surgical procedures are simulated to allow students to practice skills in a controlled environment before they work with real patients.

Ethical and Legal Aspects:
• Ethical and legal aspects, including patient consent, confidentiality, and informed decision-making, are thoroughly taught.
Mentorship:
• Mentorship is an integral part of our program, with mentors assigned to provide guidance, answer questions, and offer career advice to medical students.
Research and Journal Clubs:
• Participation in research projects and journal clubs related to specific departments is strongly encouraged, fostering a deeper understanding of evidence-based medicine.
Elective Rotations and Observerships:
• Elective rotations in specialized areas are offered, allowing students to explore their interests.
• Opportunities for students to shadow experienced practitioners are provided.
